If you work in the electrical industry, you know how important it is to follow safety regulations. One crucial part of this is understanding the NEC 250.66 chart - a tool that ensures proper grounding in alternating current systems. In this blog post, we'll explore this important chart and its role in electrical safety.
Common Pain Points
For those who are new to the electrical industry, the NEC 250.66 chart can be quite confusing. When working with alternating current systems, it's essential to ensure proper grounding for safety reasons. However, without a clear understanding of the NEC 250.66 chart, it's easy to make costly mistakes. Additionally, some electricians may find the chart's technical jargon difficult to understand.
What is the Target of NEC 250.66 Chart?
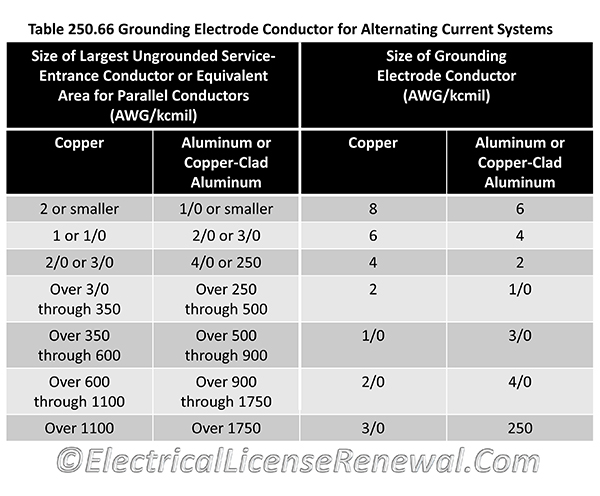
The NEC 250.66 chart specifies the minimum required size for a grounding electrode conductor based on the size of the largest circuit breaker. In other words, the chart helps electricians ensure proper grounding based on the size of the system they're working with.
Summarizing the Main Points
The NEC 250.66 chart plays a critical role in electrical safety. It ensures proper grounding by specifying the minimum size of a grounding electrode conductor based on the size of the largest circuit breaker. While the chart can be confusing for newcomers and seasoned electricians alike, it is essential to understand.
Explaining the Target of NEC 250.66 Chart
The target of the NEC 250.66 chart is to ensure safety when dealing with alternating current systems. The chart specifies the proper size for a grounding electrode conductor based on the size of the system - ensuring that the potential for electrical shocks and other dangers is minimized. As an electrician myself, I've seen firsthand the damage that can occur when safety regulations aren't followed. Proper use of the NEC 250.66 chart is non-negotiable when it comes to electrical safety.
The Importance of Proper Grounding
Proper grounding is essential for electrical safety. Inadequate grounding can result in electrical shock, fire, equipment damage, and even fatal accidents. Understanding the NEC 250.66 chart is one of the best ways for electricians to ensure proper grounding and keep themselves and those around them safe. By following the chart's specifications and guidelines, electricians can rest assured that they are doing everything in their power to maintain electrical safety standards.

Why Is the NEC 250.66 Chart So Important?
The NEC 250.66 chart is critical because it ensures proper grounding in alternating current systems. Without proper grounding, electrical currents can be unpredictable and potentially deadly. The chart also helps to prevent equipment damage and avoid costly repairs.
Exploring the NEC 250.66 Chart
The NEC 250.66 chart can be found in the National Electric Code Handbook. It specifies the minimum size required for a grounding electrode conductor based on the size of the system. The chart is organized in such a way that electricians can quickly find the appropriate size for the system they are working with. It's important to note that failure to follow the chart's guidelines could result in fines or even legal action in some cases.
Question and Answer
Q: What is the NEC 250.66 Chart?
A: The NEC 250.66 chart specifies the minimum required size for a grounding electrode conductor based on the size of the largest circuit breaker.
Q: What happens if you don't follow the NEC 250.66 guidelines?
A: Failure to follow the chart's guidelines could result in fines or legal action in certain scenarios. More importantly, improper grounding can lead to dangerous electrical shocks, fires, and other accidents.
Q: Is the NEC 250.66 chart difficult to understand?
A: For those new to the electrical industry, the chart may be confusing at first. However, with proper education and training, understanding and utilizing the chart should become second nature for all electricians.
Q: Why is proper grounding so important?
A: Improper grounding can result in dangerous electrical shocks, fires, equipment damage, and even fatal accidents. Proper grounding is essential for electrical safety.
Conclusion
The NEC 250.66 chart is an essential tool for electricians to ensure proper grounding in alternating current systems. Although the chart may be confusing at first, taking the time to understand and utilize its guidelines is non-negotiable for electrical safety. Proper grounding is critical for preventing accidents, avoiding equipment damage, and maintaining compliance with industry regulations. By utilizing the NEC 250.66 chart, electricians can rest assured that they are doing everything in their power to keep themselves and those around them safe.
Gallery
1) A 240 V, 40 A, Single Phase Load Is Located 150 Ft | Chegg.com

Photo Credit by: bing.com / 310 nec conductor phase sizing hasn
210.19(A)(1) Conductors — Minimum Ampacity And Size.
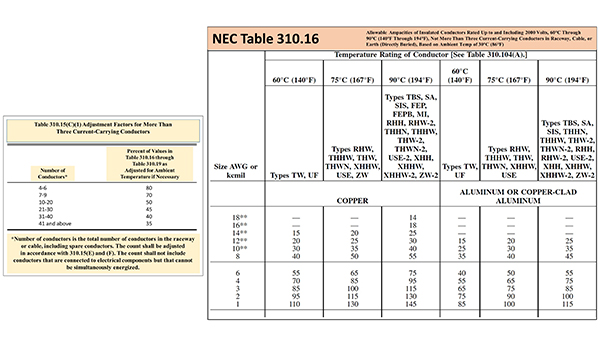
Photo Credit by: bing.com / nec ampacity conductors
250.66 Grounding Electrode Conductor For Alternating Current Systems.

Photo Credit by: bing.com /
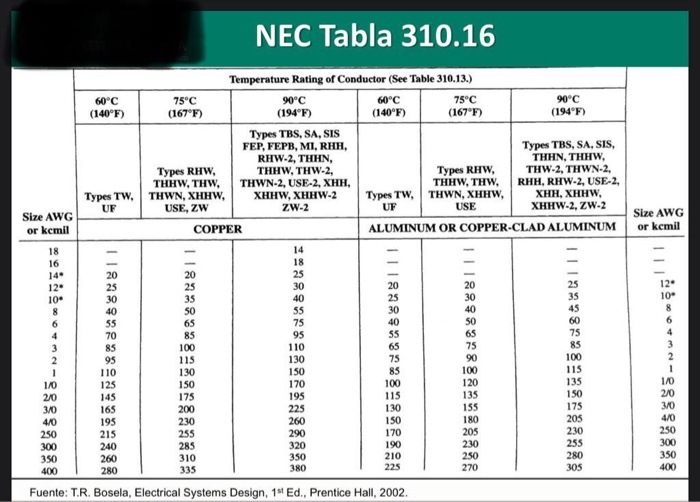
Ampacity Nec Table 310 | Brokeasshome.com

Photo Credit by: bing.com / nec 310 chart ampacity table cable conductor electrical safety
Compliant With NEC 250.24(A)(1) | The Building Code Forum

Photo Credit by: bing.com / nec compliant forum agree