The National Electric Code (NEC) is an essential safety standard that electricians follow to ensure public safety and prevent electrical hazards. One of the key areas where the NEC applies is the "tap rule." This rule has been the subject of much debate and confusion within the electrical community. In this post, we'll dive deep into the tap rule NEC and help clarify any uncertainty surrounding it.
Pain Points of Tap Rule NEC
Electricians often find it challenging to navigate the NEC's regulations on the tap rule. The complexities of this code can lead to confusion, misinterpretation, and even costly errors. The consequences of noncompliance can be severe, potentially resulting in property damage, injury, and death. As a result, it's essential to have a thorough understanding of the tap rule and how it applies to different scenarios.
Target of Tap Rule NEC
The primary purpose of the tap rule is to ensure the safety of the electrical power distribution system. The NEC mandates that feeder tap conductors not exceed a length of 10 feet and supply power to a separate piece of equipment or one other location only. The tap conductors must also have overcurrent protection in the main disconnect switch or panelboard.
Main Points on Tap Rule NEC and its Related Keywords
The tap rule is a critical component of ensuring safe power distribution. Feeder tap conductors have a maximum length of 10 feet, and overcurrent protection must be in place to meet NEC standards. Electricians and others involved in the electrical industry must understand the requirements to avoid violations and ensure public safety.
Experience with Tap Rule NEC
As an electrician, I've had many experiences working with the tap rule NEC. One particular instance was a project that involved the installation of two separate panels on the same meter. They were only a few feet apart and technically constituted one service, but I had to run a feeder tap between the two panels to comply with NEC standards. The code can be confusing, but in the end, it's all about ensuring public safety.

Clarifying Tap Rule NEC
The feeder tap rule is Section 240.21(B)(1) of the NEC and applies to the maximum length of feeder taps. The code specifies that the feeder tap conductors for two or more separate loads must not exceed 10 feet in length but can run between the separate enclosure and the protected main or feeder overcurrent device. Additionally, the tap conductors must have overcurrent protection where the tap originates.
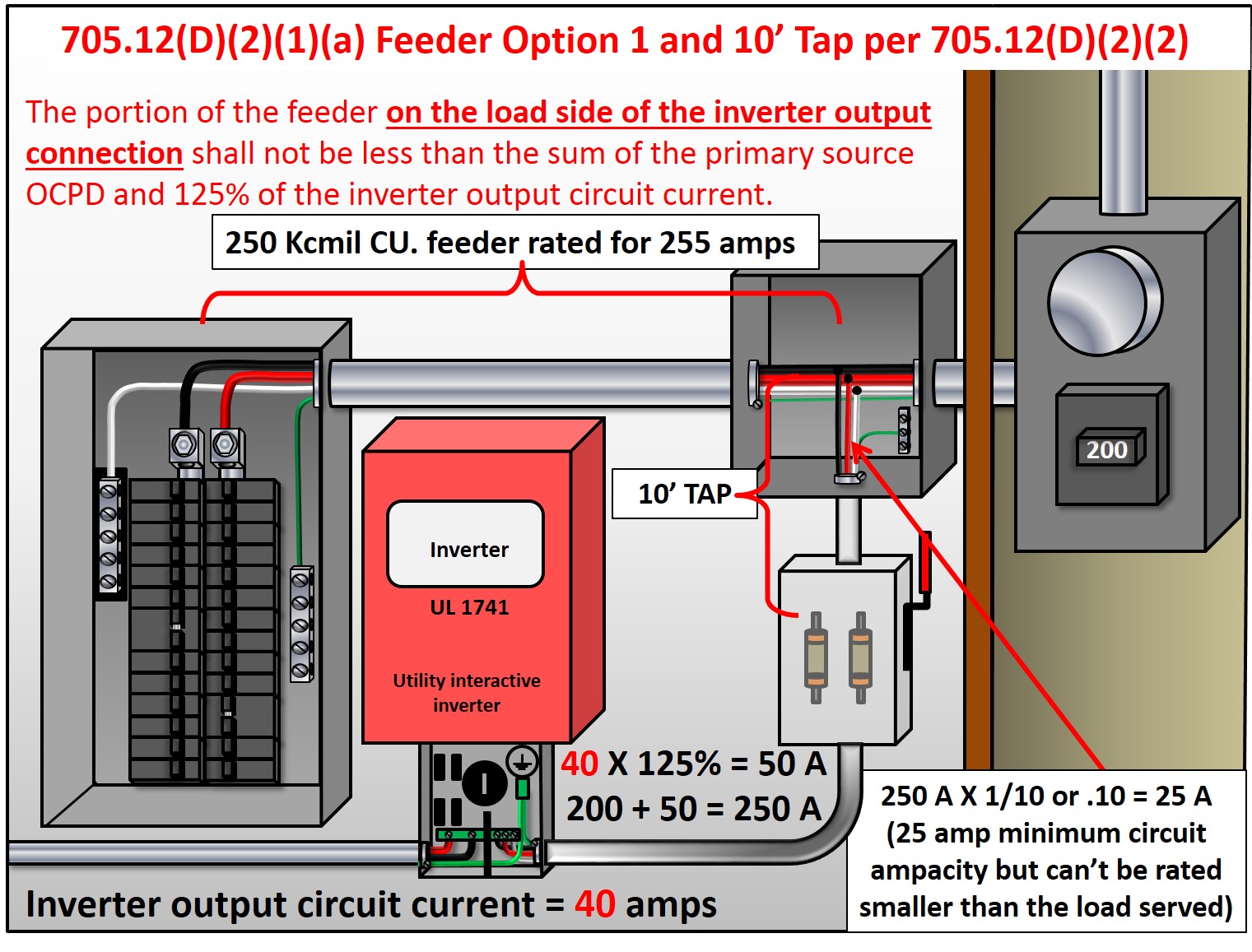
Understanding Tap Rule NEC in More Detail
The feeder tap rule plays a crucial role in ensuring electrical safety but can be difficult to understand due to the technical language of the code. One common problem area involves the maximum allowable length of the feeder tap. If the length exceeds the NEC requirements, the tap conductors may not be safely protected, and the electrical system may become overloaded, leading to equipment failure, fires, and other problems. Ensuring that the tap rule is correctly followed can prevent these issues.
Maintaining Compliance with Tap Rule NEC
Maintenance and installation of electrical systems must comply with the NEC to ensure safety, and the tap rule is no exception. Electricians and other professionals involved in the installation and maintenance of electrical systems must have a thorough understanding of the tap rule and be able to apply it correctly. Failure to do so can lead to severe legal and financial consequences, as well as potentially fatal accidents.
Question and Answer About Tap Rule NEC
Question 1: What is the purpose of the tap rule NEC?
Answer: The primary purpose of the tap rule is to ensure the safety of the electrical power distribution system. It specifies the maximum length of feeder tap conductors and requires overcurrent protection in the main disconnect switch or panelboard.
Question 2: How can electricians ensure compliance with tap rule NEC?
Answer: To ensure compliance with the tap rule NEC, electricians and other professionals involved in the installation and maintenance of electrical systems must have a thorough understanding of the code and be able to apply it effectively.
Question 3: What is the maximum length of feeder tap conductors allowed by the tap rule NEC?
Answer: The tap rule specifies that feeder tap conductors for two or more separate loads must not exceed more than 10 feet in length.
Question 4: Why is it critical to comply with tap rule NEC?
Answer: Compliance with tap rule NEC is essential to protect public safety and prevent accidents, fires, and equipment damage.
Conclusion of Tap Rule NEC
The feeder tap rule NEC plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety of the electrical power distribution system. Electricians and other professionals involved in the installation and maintenance of electrical systems must have a thorough understanding of the code and be able to apply it correctly to prevent hazardous events. Compliance is essential to protect public safety and prevent accidents and other problems from occurring.
Gallery
Stumped By The Code? NEC Requirements For 10-Ft Tap Rules | EC&M

Photo Credit by: bing.com / nec rules grounding stumped circuit bonding sizing holt ecmweb fault quandaries
Feeder1_Taps_10FT – Jade Learning

Photo Credit by: bing.com / taps feeder1 10ft nec feeder tap rule foot
240.21(B)(1) Feeder Taps Not Over 3 M (10 Ft) Long.
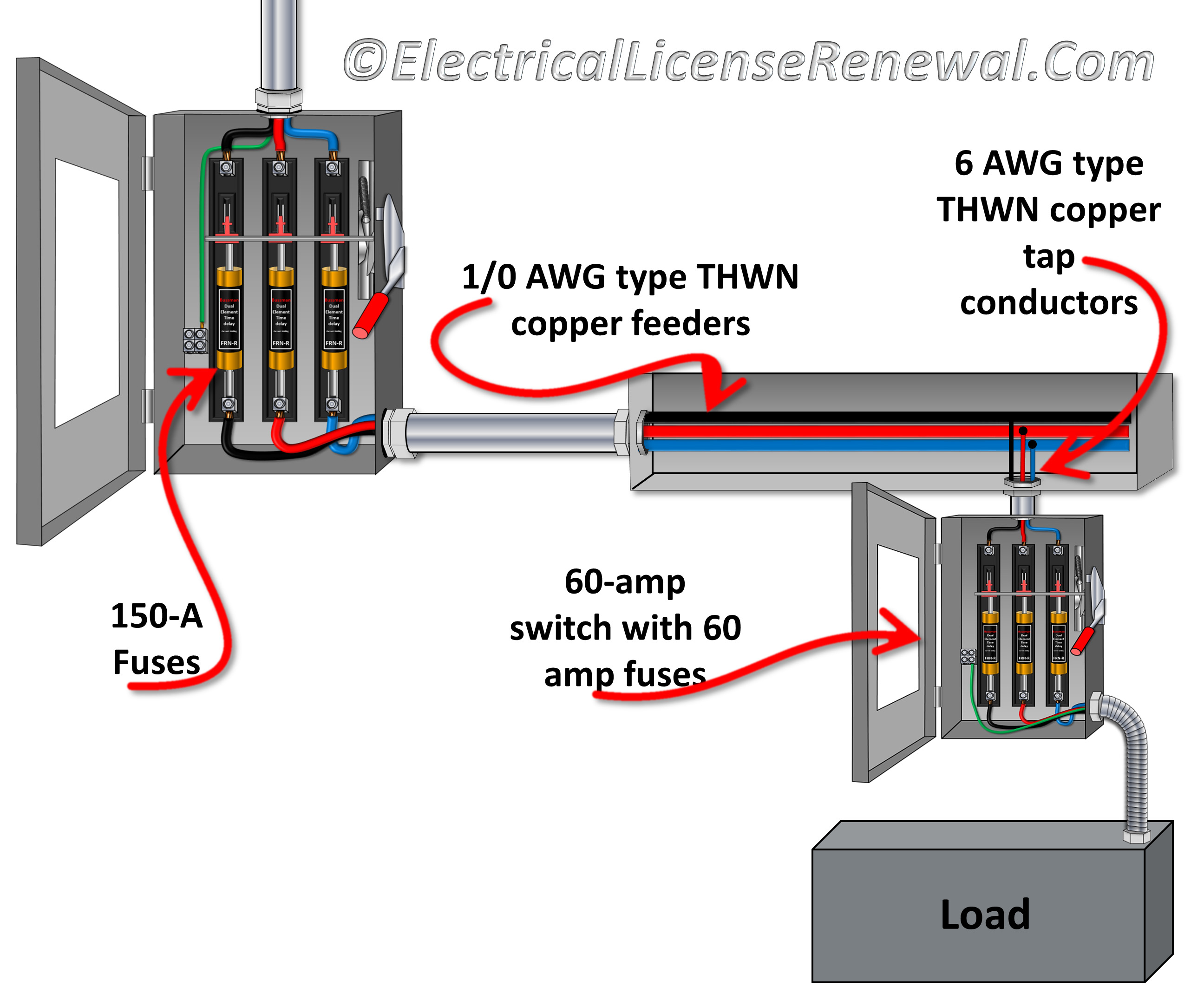
Photo Credit by: bing.com / electrical tap feeder conductor nec conductors taps overcurrent ft over device equipment supplied
2014 NEC 705.12(D)(2) PV Interconnections Part 2 – JADE Learning
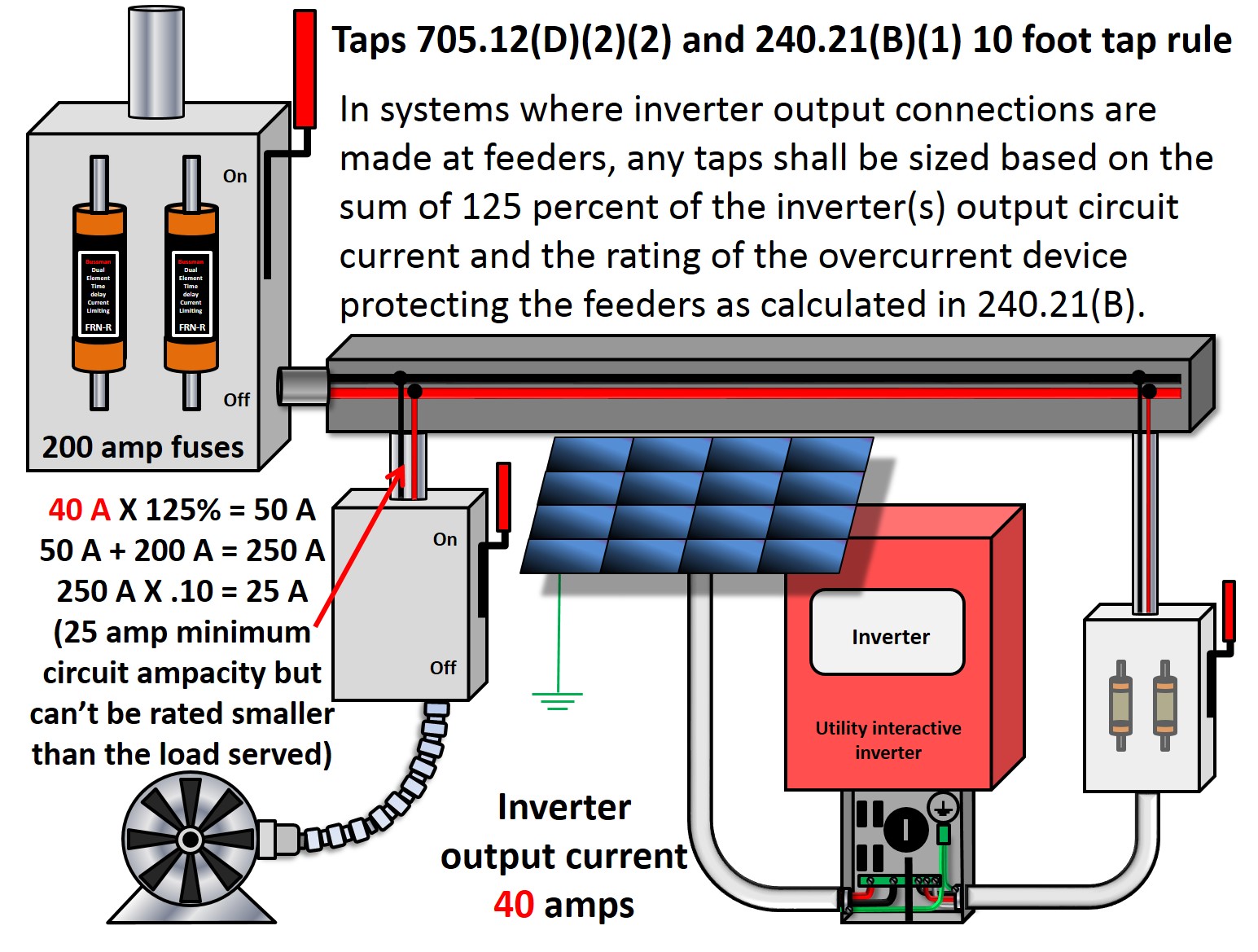
Photo Credit by: bing.com / tap rule nec foot
NEC 2011 Feeder Tap Rules 240.21(B)(1) (13min:22sec) - YouTube
Photo Credit by: bing.com / taps tap conductors outside secondary feeder nec electrical rules 240 overcurrent phase converters rotary wanting learn canadian device they