If you're an electrician, you know that NEC Chapter 9 Table 1 is one of the most important tables in the National Electrical Code (NEC). It provides crucial information about the maximum number of conductors that can be installed in a conduit or tubing, which can have a huge impact on the safety and efficiency of an electrical system.
Dealing with conduit fill can be a major pain point for electricians, especially when dealing with tight spaces or complex systems. It's vital to get conduit fill right, or you risk overloading the system and creating an unsafe situation.
So what is the target of NEC Chapter 9 Table 1? Simply put, the table provides guidelines for the maximum number of conductors that can be installed in a conduit or tubing based on the size of the conduit and the diameter of the conductors. This information is crucial for ensuring that your electrical system is safe and efficient.
In summary, NEC Chapter 9 Table 1 is a vital tool for electricians that provides guidelines for the safe and efficient installation of conductors in conduits or tubing. By following the guidelines provided in this table, electricians can ensure that their electrical systems are up to code and functioning safely.
Understanding NEC Chapter 9 Table 1
When I was first starting out as an electrician, I struggled to understand NEC Chapter 9 Table 1. It seemed like there were so many factors to consider, and I wasn't sure how to apply the information to real-world situations. But over time, I've come to appreciate the importance of this table, and I've learned how to use it effectively in my work.
So what does NEC Chapter 9 Table 1 actually tell us? Essentially, the table provides guidelines for the maximum number of conductors that can be installed in a conduit or tubing based on the size of the conduit and the diameter of the conductors. This information is crucial for ensuring that the electrical system is safe and efficient, and it's essential for compliance with the National Electrical Code.
To use NEC Chapter 9 Table 1 effectively, you'll need to understand some key terms. The most important term is "conduit fill," which refers to the amount of space inside a conduit or tubing that is occupied by conductors. The more conductors you have in a given space, the more crowded the conduit will be, and the more likely it is that there will be problems with overheating or other safety issues.
Another important term to understand is "conduit size," which refers to the diameter of the conduit or tubing. This is important because the size of the conduit determines how much space there is for conductors. For example, a larger conduit will be able to hold more conductors than a smaller conduit.
How to Use NEC Chapter 9 Table 1
Using NEC Chapter 9 Table 1 effectively requires a bit of math and careful planning. First, you'll need to determine the size of the conduit or tubing you're working with, as well as the diameter of the conductors you'll be installing. Then, you can consult the table to determine the maximum number of conductors that can be installed in that space.
For example, let's say you're working with a 3/4-inch conduit and 12-gauge conductors. Consulting NEC Chapter 9 Table 1, you'll find that the maximum number of conductors for this setup is 16. If you need to install more than 16 conductors, you'll need to use a larger conduit or split the conductors into multiple conduits.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
While NEC Chapter 9 Table 1 is an essential tool for electricians, there are some common mistakes to avoid when using it. One of the most common mistakes is failing to account for different types of conductors. For example, some conductors have thicker insulation than others, which can affect how much space they take up in a conduit.
Another mistake to avoid is assuming that you can always fill a conduit or tubing to the maximum allowed by the table. While the table provides maximums, it's often a good idea to leave some extra space in the conduit for future expansions or modifications.
Question and Answer
Q: What is conduit fill?
A: Conduit fill refers to the amount of space inside a conduit or tubing that is occupied by conductors.
Q: How do I determine the maximum number of conductors for my conduit?
A: Consult NEC Chapter 9 Table 1 and input the size of the conduit and the diameter of the conductors to determine the maximum number of conductors allowed.
Q: What happens if I exceed the maximum number of conductors allowed by NEC Chapter 9 Table 1?
A: Exceeding the maximum number of conductors can create an unsafe situation due to overheating or other issues. It's important to follow NEC guidelines to ensure safety and compliance.
Q: Can I ever fill a conduit or tubing to the maximum allowed by the table?
A: While the table provides maximums, it's a good idea to leave some extra space in the conduit for future expansions or modifications.
Conclusion
NEC Chapter 9 Table 1 is a crucial tool for electricians that provides guidelines for the safe and efficient installation of conductors in conduits or tubing. By understanding how to use this table effectively and avoiding common mistakes, electricians can ensure that their electrical systems are up to code and functioning safely.
Gallery
NEC Chapter 9 Table 9.pdf | Electrical Conductor | Electrical Impedance

Photo Credit by: bing.com / nec chapter table pdf
Conduit Fill Table Nec | Awesome Home
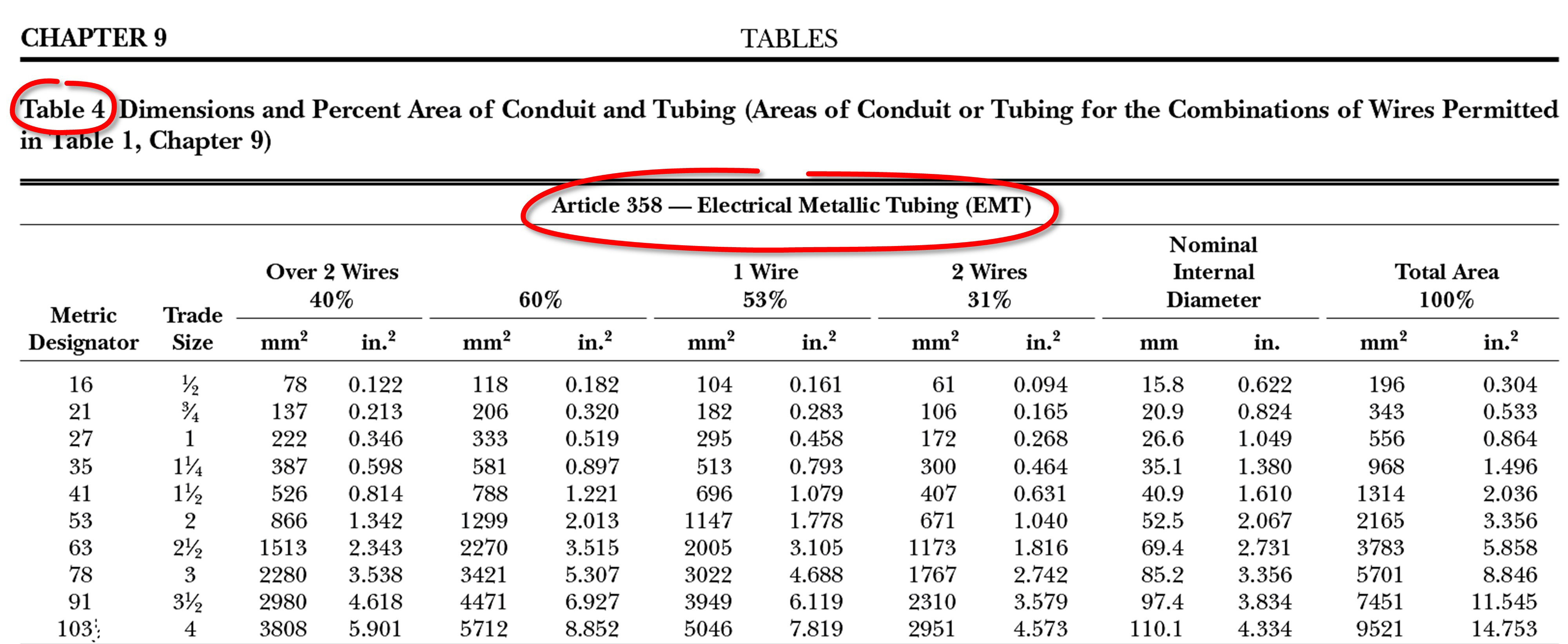
Photo Credit by: bing.com /
19+ Chapter 9 Table 9 Nec | NenehNavjeet
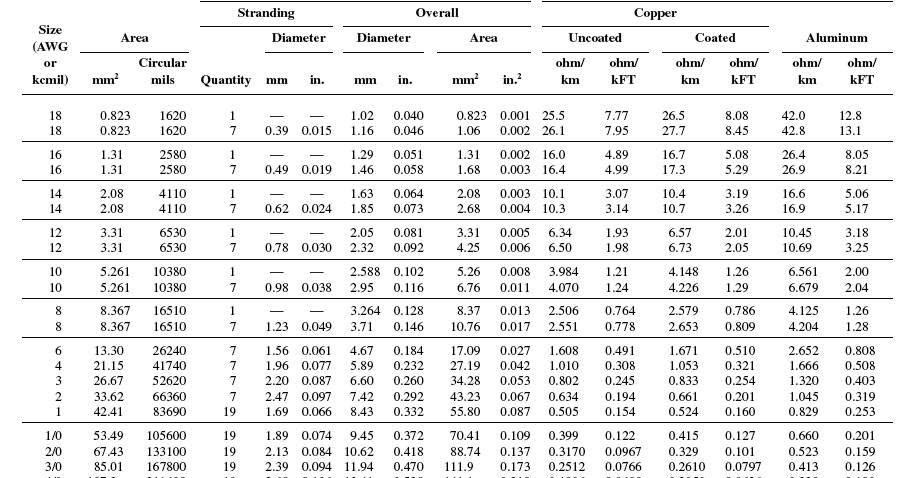
Photo Credit by: bing.com /
Nec Wire Fill Chart Emt - Wiring Draw

Photo Credit by: bing.com /
Electrical Engineering
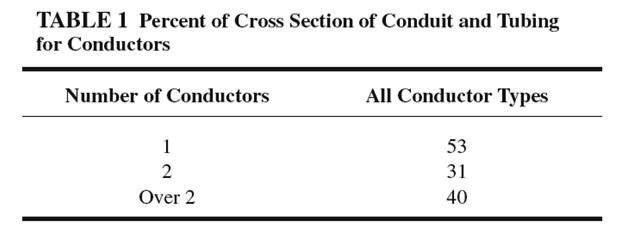
Photo Credit by: bing.com / conduit fill table chapter electrical calculations annex informational note tubing